What Does an Inverted Yield Curve Look Like?
This article is part of our guide on buying real estate during a recession, available here.
The yield curve is considered one of the most reliable predictors of a recession. That’s why alarms go off when the narrowing plot points turn a healthy curve into an inverted curve. What does an inverted yield curve look like? That’s precisely what we’ll cover in this post!
Key Takeaways
-
A yield curve becomes inverted when long-term interest rates drop below short-term interest rates.
-
This inversion indicates that investors are shifting their money from short-term to long-term bonds. Why is this negative? The short answer is that it reflects deep pessimism about the economy in the near future.
-
According to analysts, the inversion of the yield curve has occurred 28 times since 1900.
What does Yield Curve Inversion Mean?
Yield curves illustrate the interest rates on Treasury market bonds of increasing maturities. When yield curves invert, short-term debt instruments carry higher yields than long-term instruments with the same risk profile.
This is uncommon. In “normal” economic times, long-term debt should carry greater risk with higher interest rates than short-term debt. Next, we’ll explain how an inverted yield curve looks different from a healthy yield curve.
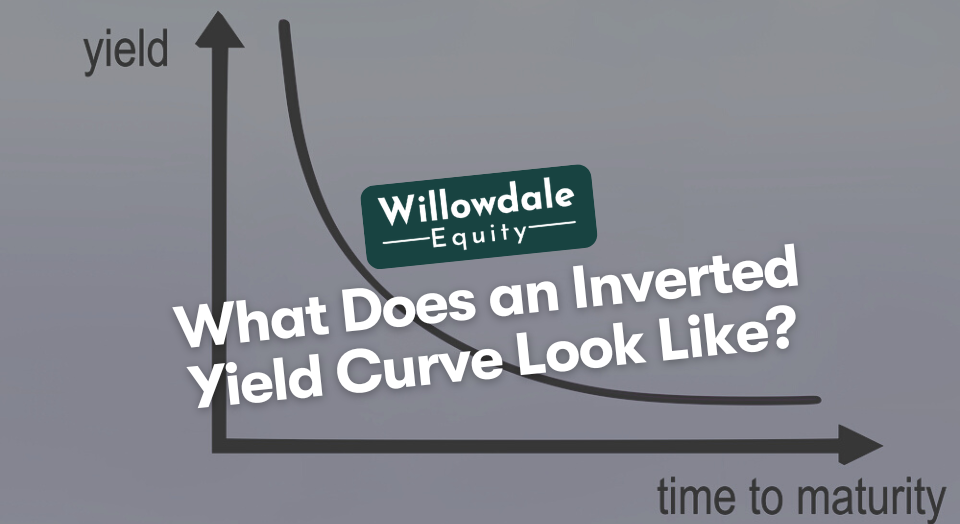
What does an Inverted Yield Curve Look Like?
A yield curve becomes inverted when long-term interest rates drop below short-term interest rates. This inversion indicates that investors are shifting their money from short-term to long-term bonds. Why is this negative? The short answer is that it reflects deep pessimism about the economy in the near future.
When a yield curve is healthy, it slopes upward as a reflection of short-term interest rates being lower than long-term interest rates. As the spread between the two shrinks, the curve begins to flatten. Flattened curves typically progress into inverted curves. Next, I’ll cover some of the reasons why yield curves invert.
Why Would a Yield Curve Invert?
Pessimism is the ultimate answer behind why inverted yield curves happen. A scramble to preserve capital often produces inverted yield curves when market indicators look worrisome. Investors famously favor long-term treasury bonds when concerns of recession loom. These bonds are considered safe harbors that provide protection against plummeting equities markets.
When long-term maturities see major rotations caused by this scramble, it’s common for long-term rates to dip below short-term rates. This is where the curve happens. How panicked should you be when you see an inverted yield curve?
How Many Times has the Yield Curve Inverted?
According to analysts, the inversion of the yield curve has occurred 28 times since 1900. However, the current economic climate has seen two back-to-back inversions worth discussing. We’ll cover the most recent inversion next.
When was the last Yield Curve Inversion?
The most recent yield curve inversion occurred on April 1, 2022. This was the day that the 10-year Treasury note’s yield dipped below the yield of the two-year Treasury note. Those who have been watching the stock market closely may recall a previous inversion in 2019 just before a mini-recession triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Another inverted yield curve lasted from December 2005 into the middle of 2007, preceding the Great Recession of 2008. Does that mean that an inverted yield curve always predicts a recession? We’ll show you what the track record looks like next.
Related Read: What Happens to Real Estate if the Stock Market Crashes?
Why does an Inverted Yield Curve Predict a Recession?

As we shared earlier, an inverted Treasury yield curve predicts a recession because it’s a barometer of investors’ pessimism over the near future of economic growth. Just how accurate is the inverted yield curve for predicting a recession? According to a report from the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, the yield curve has inverted before each recession since 1955. A recession typically follows six and 24 months after the yield curve inverts.
Yield curves affect both consumers and businesses. Lenders tend to batten down the hatches on lending during periods of inversion. An increase in short-term Treasury bond rates often leads to higher interest for commercial loans, small business loans, and other forms of credit. This makes the cost of borrowing money higher for both consumers and businesses. In addition, higher interest rates can make mortgages less attainable.
Let’s roll through some commonly asked questions about yield curve inversion and real estate.
Frequently Asked Questions About Yield Curve Inversion Real Estate
A normal Treasury yield curve slopes upward to reflect that short-term interest rates are lower than long-term interest rates. As differences in rates narrow, you’ll see a flattening effect that often leads to an inverted curve that sounds the alarms for economic troubles.
Yield curve inversion indicates economic pessimism among investors. In addition, a yield curve is seen as a strong indicator of an impending recession. The yield curve has inverted before each recession since 1955.
What an Inverted Yield Curve Looks Like - Conclusion
An inverted yield curve plots the reversal of short-term debt having lower interest rates than long-term debt. Economic recession and tighter lending can mean big things for the real estate and rental markets. There’s no doubt that getting in a position to pivot to some secure assets can make all the difference for investors. Join the investor club at Willowdale Equity to learn how investors hedge against inverted yield curves and recessions through private multifamily investments.
Sources:
- Reuters, “Explainer: U.S. yield curve inverts again: What is it telling us?“
- Reuters, “Shares bounce, US yield curve inverts after strong jobs data“
- Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, “Economic Forecasts with the Yield Curve“
Interested In Learning More About PASSIVE Real Estate Investing In Multifamily Properties?
Get Access to the FREE 5 Day PASSIVE Real Estate Investing Crash Course.
In this video crash course, you’ll learn everything you need to know from A to Z
about passive investing in multifamily real estate.
We’ll cover topics like earned income vs passive income, the tax advantages, why multifamily, inflation, how syndications work, and much much more!